Lyophilized Semaglutide in Research: A Researcher's Perspective
2024-07-04
As a researcher working with lyophilized semaglutide, here's my experience and understanding:
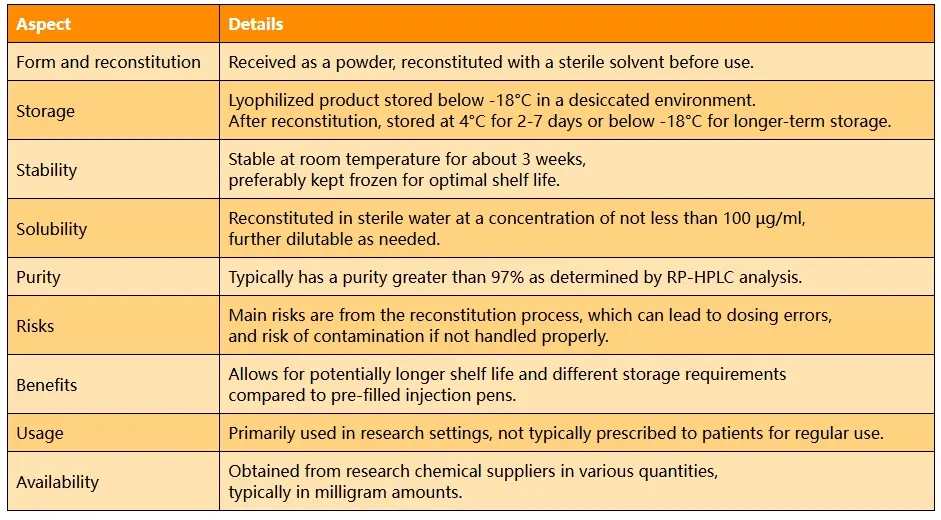
- Form and reconstitution: I receive it as a powder that I need to reconstitute with a sterile solvent before use.
- Storage: I typically store the lyophilized product below -18°C in a desiccated environment. After reconstitution, I keep it at 4°C for 2-7 days or below -18°C for longer-term storage.[1]
- Stability: While it's stable at room temperature for about 3 weeks, I prefer to keep it frozen for optimal shelf life.[2]
- Solubility: I usually reconstitute it in sterile water at a concentration of not less than 100 µg/ml, which I can further dilute as needed.[3]
- Purity: The lyophilized form I use typically has a purity greater than 97% as determined by RP-HPLC analysis.[4]
- Risks: In my experience, the main risks come from the reconstitution process, which can lead to dosing errors if not done correctly. There's also a risk of contamination if not handled properly.[5]
- Benefits: Compared to pre-filled injection pens, I find this form allows for potentially longer shelf life and different storage requirements.[6]
- Usage: I primarily use it in research settings, and it's not the typical form prescribed to patients for regular use.[7]
- Availability: I usually obtain it from research chemical suppliers in various quantities, typically in milligram amounts.[8]
When handling lyophilized semaglutide, I always follow proper reconstitution procedures and storage guidelines carefully to maintain its efficacy and safety. I use this form mainly in research environments rather than for routine patient care.
It's worth noting that for clinical use, semaglutide is typically administered as a subcutaneous injection using pre-filled pens, with dosages ranging from 0.25 mg to 2 mg depending on the specific treatment regimen.[9]
References
- Storage and stability of lyophilized semaglutide
- Temperature stability of semaglutide
- Reconstitution guidelines for lyophilized semaglutide
- Purity analysis of lyophilized semaglutide
- Risks associated with semaglutide reconstitution
- Comparison of lyophilized and pre-filled semaglutide formulations
- Research applications of lyophilized semaglutide
- Sourcing lyophilized semaglutide for research
- Clinical use of semaglutide: dosage and administration

 USD
USD




